Browser Object Model
Day 21: 60 Days Of Full Stack Web Development Challenge
The Browser Object Model (BOM) is used to interact with the browser.
This enables access & manipulation of the browser window, frames, and other browser-related objects by facilitating the JavaScript code.
The default object of browser is window means you can call all the functions of window by specifying window or directly
window.alert(" Hey Geeks");
// Same as
alert(" Hey Geeks ");
It is not recommended always to explicitly mention “window” because it’s the default. So, the alert(” Hey Geeks “); is equivalent to the longer version.
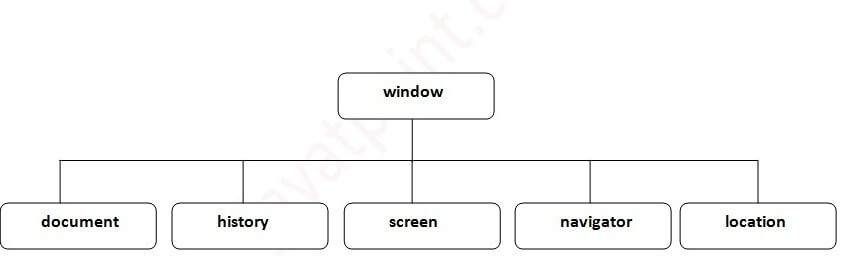
Browser Object Model Types :
| Types | Description |
| Window Object Model | Represents the browser window and serves as the main tool for interaction within the Browser Object Model (BOM). |
| History Object Model | Enables navigation control by keeping track of the user’s browsing history in the Browser Object Model (BOM). |
| Screen Object Model | Offers information about the user’s screen, like its size, within the Browser Object Model (BOM). |
| Navigator Object Model | Provides details about the user’s browser and system characteristics within the Browser Object Model (BOM). |
| Location Object Model | Manages the current web address (URL) and allows changes within the Browser Object Model (BOM). |
Advantages & Disadvantages of BOM :
Advantages
User Interaction: BOM allows websites to show alerts, prompts, and confirmations, making them more interactive.
Navigation Control: It also helps to manage going back or forward in your browsing history using tools like ‘history.’
Browser Details: BOM gives information about your browser through the ‘navigator’ tool, helping to adjust content for different browsers and systems.
Location Management: Using the ‘location’ tool, BOM lets websites change web addresses for dynamic content and easy redirection.
Disadvantages
Browser Compatibility: It may work differently in various browsers, causing compatibility issues.
Security Concerns: Some BOM features, like pop-ups, can be exploited for security risks.
Client-Side Dependency: It relies heavily on the client side, hence affecting performance.
Limited Standardization: It lacks a standardized specification, leading to variations in implementation.
Window Object :
The window object represents a window in browser.
An object of window is created automatically by the browser.
Window is the object of browser, it is not the object of javascript.
The javascript objects are string, array, date etc.
Methods of window object :
The important methods of window object are as follows:
| Method | Description |
| alert() | displays the alert box containing message with ok button. |
| confirm() | displays the confirm dialog box containing message with ok and cancel button. |
| prompt() | displays a dialog box to get input from the user. |
| open() | opens the new window. |
| close() | closes the current window. |
| setTimeout() | performs action after specified time like calling function, evaluating expressions etc. |
Example of alert() in javascript
It displays alert dialog box. It has message and ok button.
<script type="text/javascript">
function msg(){
alert("Hello Alert Box");
}
</script>
<input type="button" value="click" onclick="msg()"/>
History Object :
The JavaScript history object represents an array of URLs visited by the user.
By using this object, you can load previous, forward or any particular page.
The history object is the window property, so it can be accessed by:
window.history
Or
history
Property of JavaScript history object :
There are only 1 property of history object.
| No. | Property | Description |
| 1 | length | returns the length of the history URLs. |
Methods of JavaScript history object :
There are only 3 methods of history object.
| No. | Method | Description |
| 1 | forward() | loads the next page. |
| 2 | back() | loads the previous page. |
| 3 | go() | loads the given page number. |
Example of history object :
Let’s see the different usage of history object
history.back();//for previous page
history.forward();//for next page
history.go(2);//for next 2nd page
history.go(-2);//for previous 2nd page
Navigator Object :
The JavaScript navigator object is used for browser detection.
It can be used to get browser information such as appName, appCodeName, userAgent etc.
The navigator object is the window property, so it can be accessed by
window.navigator
Or
navigator
Property of JavaScript navigator object :
There are many properties of navigator object that returns information of the browser.
| No. | Property | Description |
| 1 | appName | returns the name |
| 2 | appVersion | returns the version |
| 3 | appCodeName | returns the code name |
| 4 | cookieEnabled | returns true if cookie is enabled otherwise false |
| 5 | userAgent | returns the user agent |
| 6 | language | returns the language. It is supported in Netscape and Firefox only. |
| 7 | userLanguage | returns the user language. It is supported in IE only. |
| 8 | plugins | returns the plugins. It is supported in Netscape and Firefox only. |
| 9 | systemLanguage | returns the system language. It is supported in IE only. |
| 10 | mimeTypes[] | returns the array of mime type. It is supported in Netscape and Firefox only. |
| 11 | platform | returns the platform e.g. Win32. |
| 12 | online | returns true if browser is online otherwise false. |
Methods of JavaScript navigator object :
The methods of navigator object are given below.
| No. | Method | Description |
| 1 | javaEnabled() | checks if java is enabled. |
| 2 | taintEnabled() | checks if taint is enabled. It is deprecated since JavaScript 1.2. |
Example:
<html>
<body>
<h2>JavaScript Navigator Object</h2>
<script>
document.writeln("<br/>navigator.appCodeName: "+navigator.appCodeName);
document.writeln("<br/>navigator.appName: "+navigator.appName);
document.writeln("<br/>navigator.appVersion: "+navigator.appVersion);
document.writeln("<br/>navigator.cookieEnabled: "+navigator.cookieEnabled);
document.writeln("<br/>navigator.language: "+navigator.language);
document.writeln("<br/>navigator.userAgent: "+navigator.userAgent);
document.writeln("<br/>navigator.platform: "+navigator.platform);
document.writeln("<br/>navigator.onLine: "+navigator.onLine);
</script>
</body>
</html>
Output:

Screen Object :
The JavaScript screen object holds information of browser screen.
It can be used to display screen width, height, colorDepth, pixelDepth etc.
The navigator object is the window property, so it can be accessed by:
window.screen Or screen
Property of JavaScript Screen Object :
There are many properties of screen object that returns information of the browser.
| No. | Property | Description |
| 1 | width | returns the width of the screen |
| 2 | height | returns the height of the screen |
| 3 | availWidth | returns the available width |
| 4 | availHeight | returns the available height |
| 5 | colorDepth | returns the color depth |
| 6 | pixelDepth | returns the pixel depth. |
Example of JavaScript Screen Object
Let’s see the different usage of screen object.
<html>
<body>
<script>
document.writeln("<br/>screen.width: "+screen.width);
document.writeln("<br/>screen.height: "+screen.height);
document.writeln("<br/>screen.availWidth: "+screen.availWidth);
document.writeln("<br/>screen.availHeight: "+screen.availHeight);
document.writeln("<br/>screen.colorDepth: "+screen.colorDepth);
document.writeln("<br/>screen.pixelDepth: "+screen.pixelDepth);
</script>
</body>
</html>
Output:

Whats Next ?
Document Object Model (DOM)
