What Is CSS ?
CSS stands for Cascading Style Sheet.
CSS is used to design HTML tags.
CSS is a widely used language on the web.
HTML, CSS and JavaScript are used for web designing. It helps the web designers to apply style on HTML tags.
Why use CSS ?
Solves a big problem
Saves a lot of time
Provide more attributes
CSS Syntax :
A CSS rule set contains a selector and a declaration block.
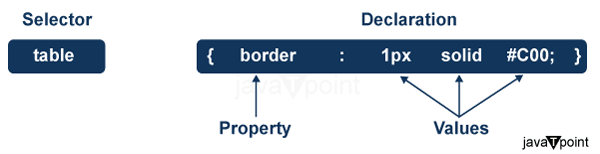
Selector:
Selector indicates the HTML element you want to style.
It could be any tag like <h1>, <title> etc.
Declaration Block:
The declaration block can contain one or more declarations separated by a semicolon.
For the above example, there are two declarations:
color: yellow;
font-size: 11 px;
Each declaration contains a property name and value, separated by a colon.
Property:
A Property is a type of attribute of HTML element.
It could be color, border etc.
Value:
Values are assigned to CSS properties.
In the above example, value "yellow" is assigned to color property.
Types Of CSS :
CSS is added to HTML pages to format the document according to information in the style sheet.
There are three ways to insert CSS in HTML documents.
Inline CSS
Internal CSS
External CSS
Inline CSS :
An inline CSS is used to apply a unique style to a single HTML element.
An inline CSS uses the
styleattribute of an HTML element.
Syntax :
<htmltag style="cssproperty1:value; cssproperty2:value;"\></htmltag>
The following example sets the text color of the <h1> element to blue, and the text color of the <p> element to red:
Example:
<h1 style="color:blue;">A Blue Heading</h1>
<p style="color:red;">A red paragraph.</p>
Output:

Disadvantages of Inline CSS :
You cannot use quotations within inline CSS. If you use quotations the browser will interpret this as an end of your style value.
These styles cannot be reused anywhere else.
These styles are tough to be edited because they are not stored at a single place.
It is not possible to style pseudo-codes and pseudo-classes with inline CSS.
Inline CSS does not provide browser cache advantages.
Internal CSS :
An internal CSS is used to define a style for a single HTML page.
An internal CSS is defined in the
<head>section of an HTML page, within a<style>element.
How to Use Internal CSS ?
To use internal CSS, include CSS rules within a <style> tag inside the HTML document’s <head>. Define styles by selecting HTML elements or classes, and applying styling rules within the tag. All the changes done by the internal CSS can be applied only to a single web page.
Syntax:
<style>
/* Internal CSS starts here */
</style>
Example:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
body {background-color: powderblue;}
h1 {color: blue;}
p{color: red;}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1>This is a heading</h1>
<p>This is a paragraph.</p>
</body>
</html>
Output:

Advantages of Internal CSS :
Internal CSS retains styles in the HTML file, avoiding conflicts with other pages and making easier management of styles at the local level.
Internal CSS has higher specificity than external CSS, which allows you to override external styles more easily within the same HTML file.
Internal CSS reduces HTTP requests, enhancing performance.
Internal CSS is relatively easy to implement, we can use class and ID selectors in this style sheet.
Disadvantages of Internal CSS :
Repetition in HTML files.
Increased file size.
Reduced code reusability.
Limited style management across pages.
External CSS :
An external style sheet is used to define the style for many HTML pages.
To use an external style sheet, add a link to it in the
<head>section of each HTML page.External CSS is used to style multiple HTML pages with a single style sheet.
External CSS contains a separate CSS file with a .css extension.
The CSS file contains style properties added on selectors (For example class, id, heading, … etc.).
How to Link a CSS File to an HTML File ?
To link a CSS file to an HTML file, use the <link> element within the HTML file’s <head> section with the rel attribute set to “stylesheet” and the href attribute specifying the CSS file’s path.
CSS property is written in a separate file with a .css extension and should be linked to the HTML document using a link tag. External CSS sets styles for elements once and applies them consistently across multiple web pages, ensuring a unified design.
Example:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="styles.css">
</head>
<body>
<h1>This is a heading</h1>
<p>This is a paragraph.</p>
</body>
</html>
Output:

Advantages of External CSS
Improved maintainability and code organization.
Enhanced reusability across multiple HTML files.
Efficient caching and faster page load times.
Disadvantages of External CSS
Pages may not render correctly until the external CSS is loaded.
Uploading or linking to multiple CSS files may increase your site’s download time, affecting its overall performance.
Large-scale projects may face versioning and caching challenges when using external CSS
CSS Comments:
CSS comments are generally written to explain your code.
It is very helpful for the users who reads your code so that they can easily understand the code.
Comments are ignored by browsers.
Comments are single or multiple lines statement and written within
/*............*/ .
